234 produits
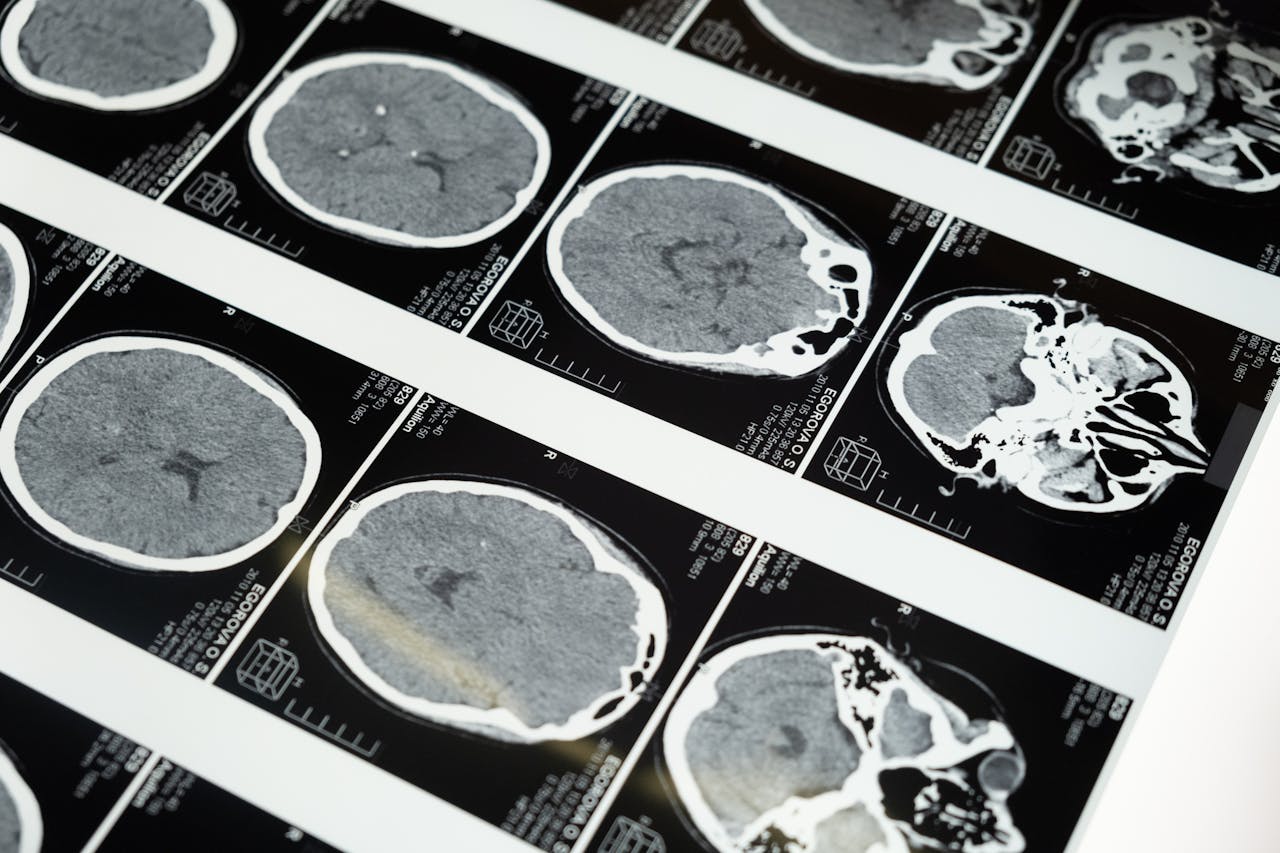
Why are non-magnetic fasteners needed?

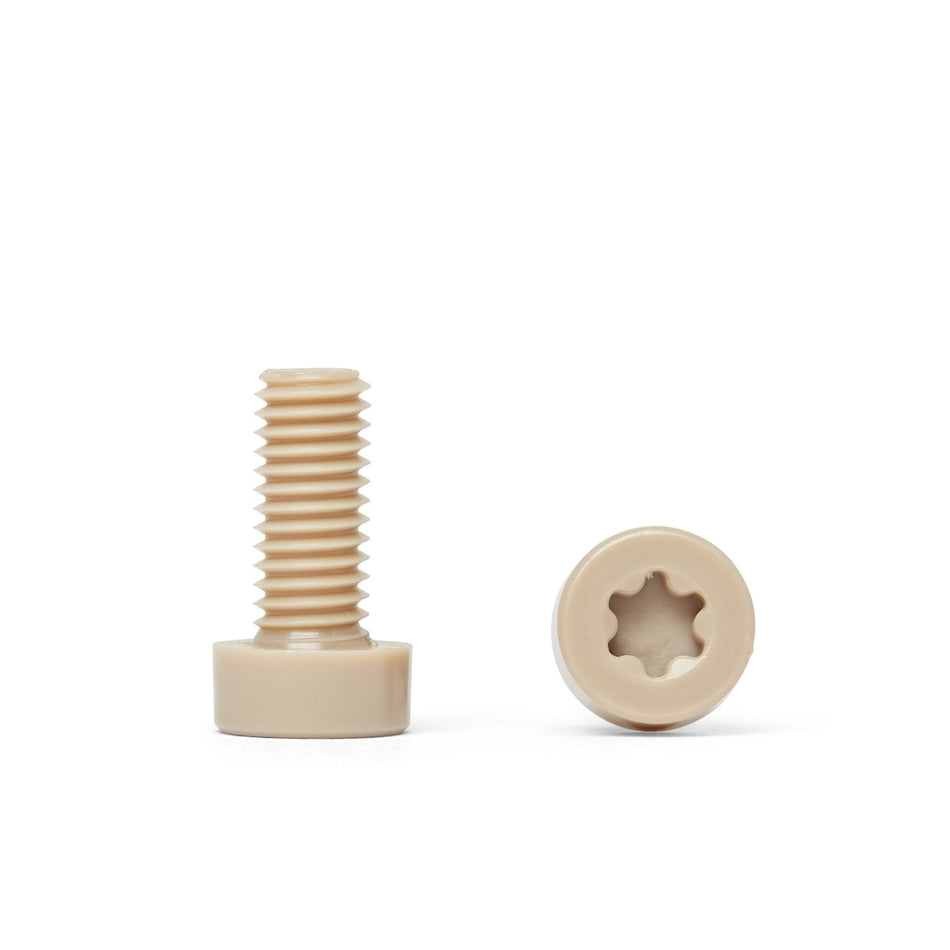
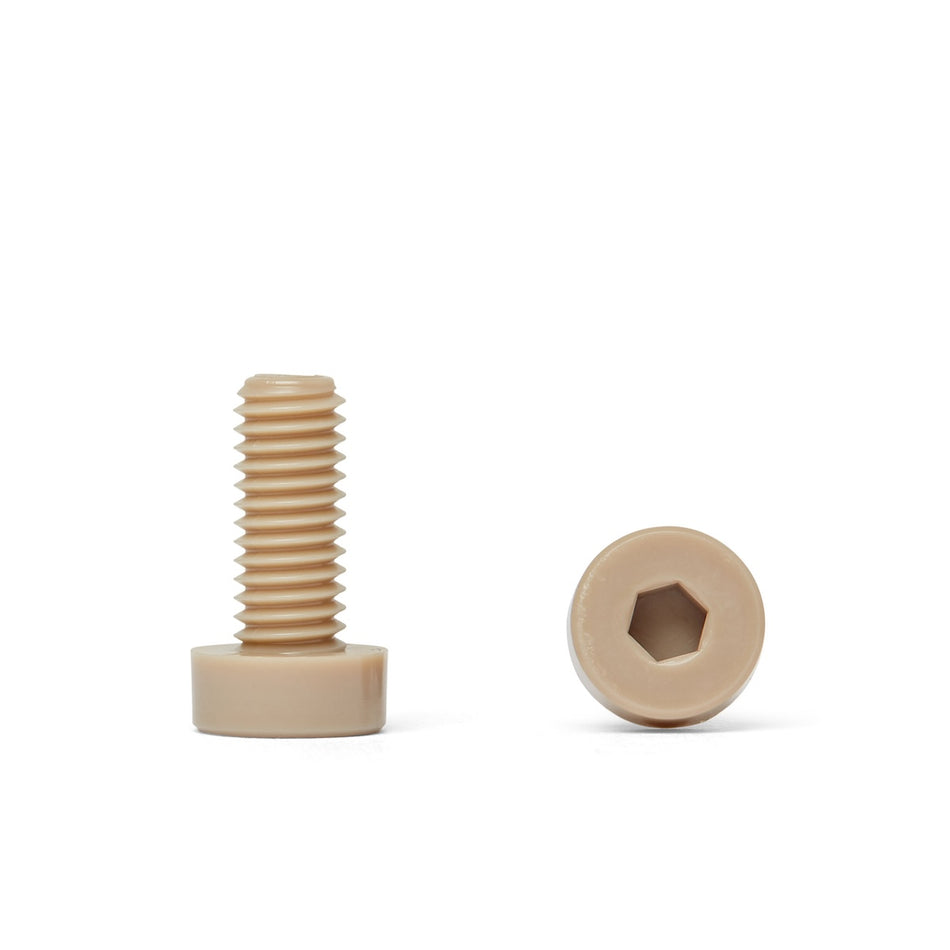
Non-Magnetic Fastener Materials
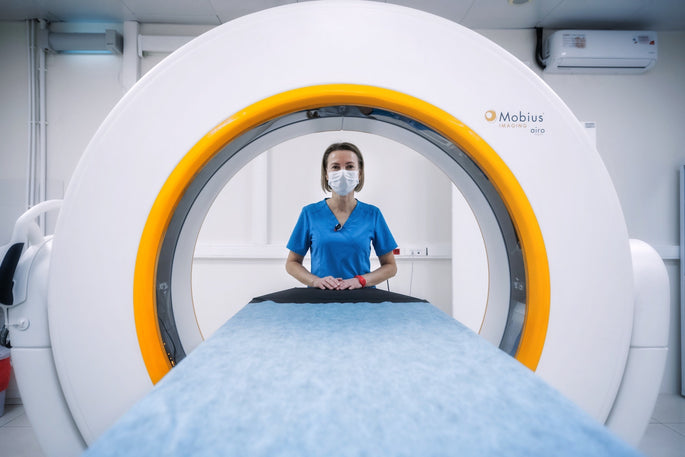
Non-Magnetic Fastener Applications
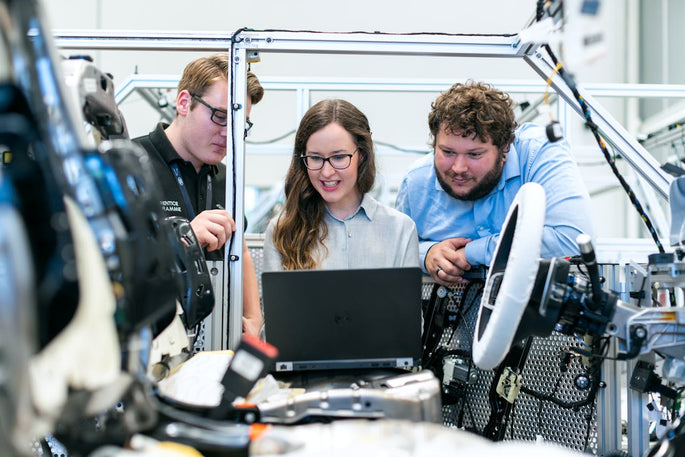

What makes these polymers non-magnetic?

What are the benefits of non-magnetic fasteners?
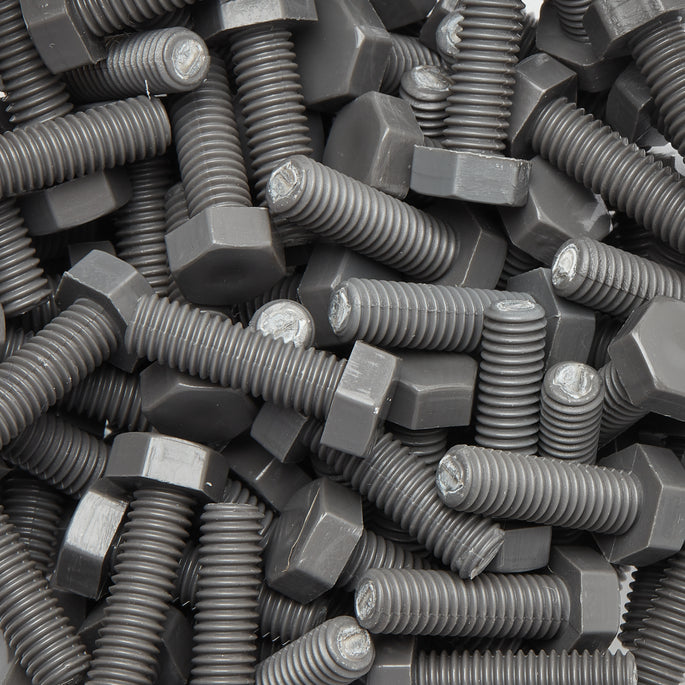

Other Benefits Of Non-Magnetic Fasteners
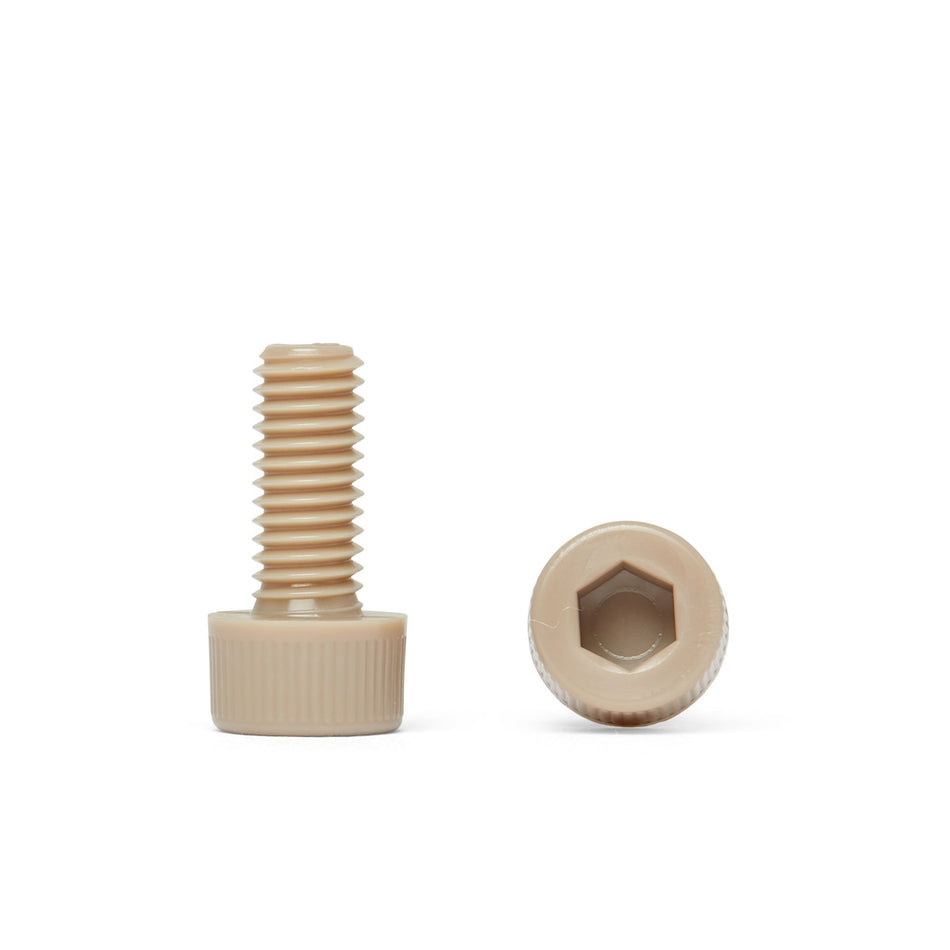
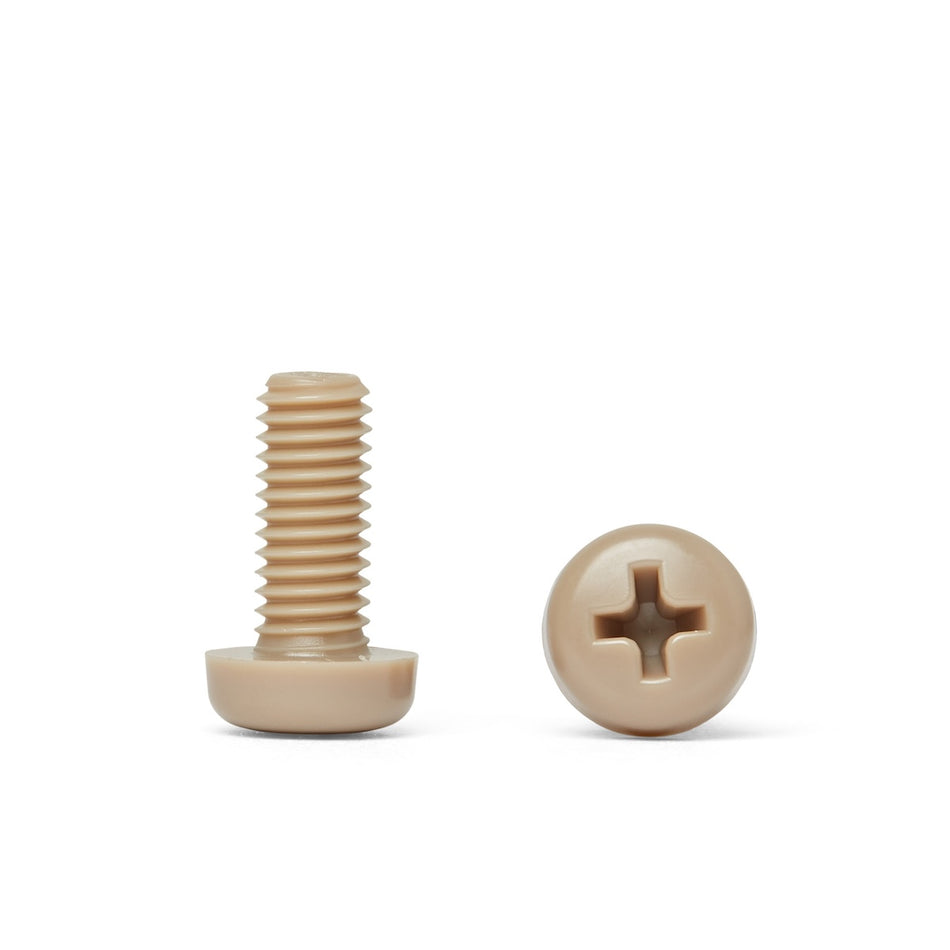
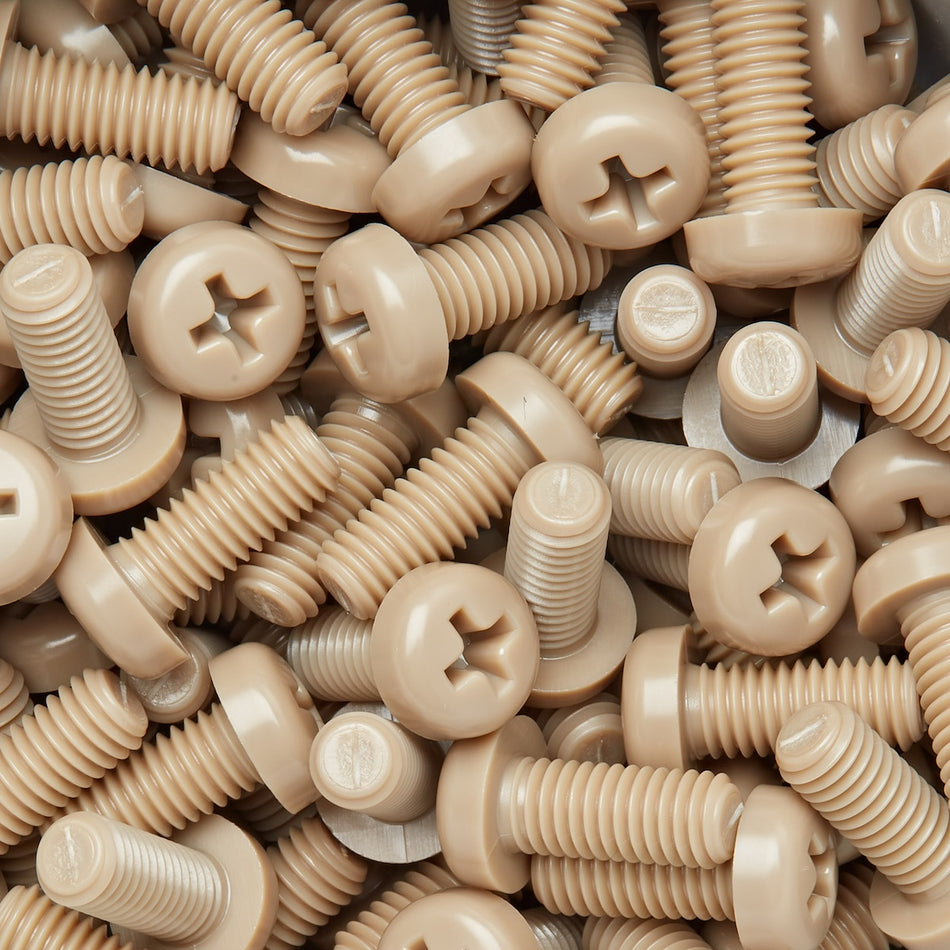
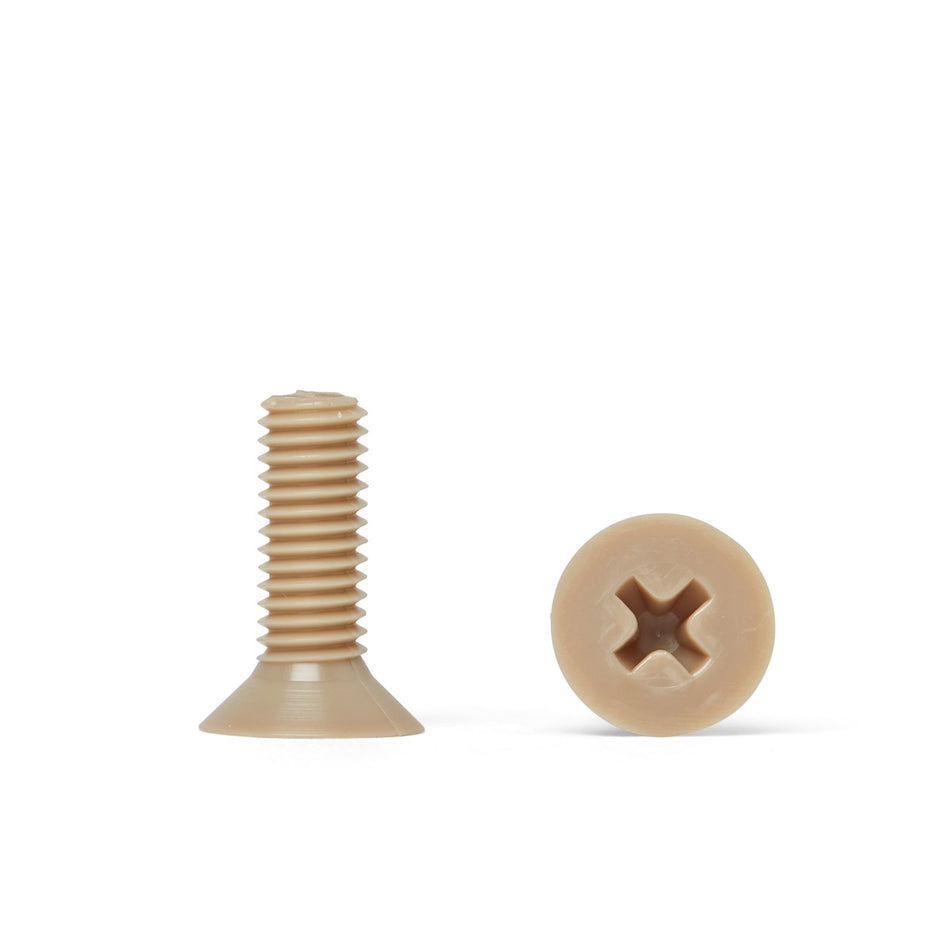
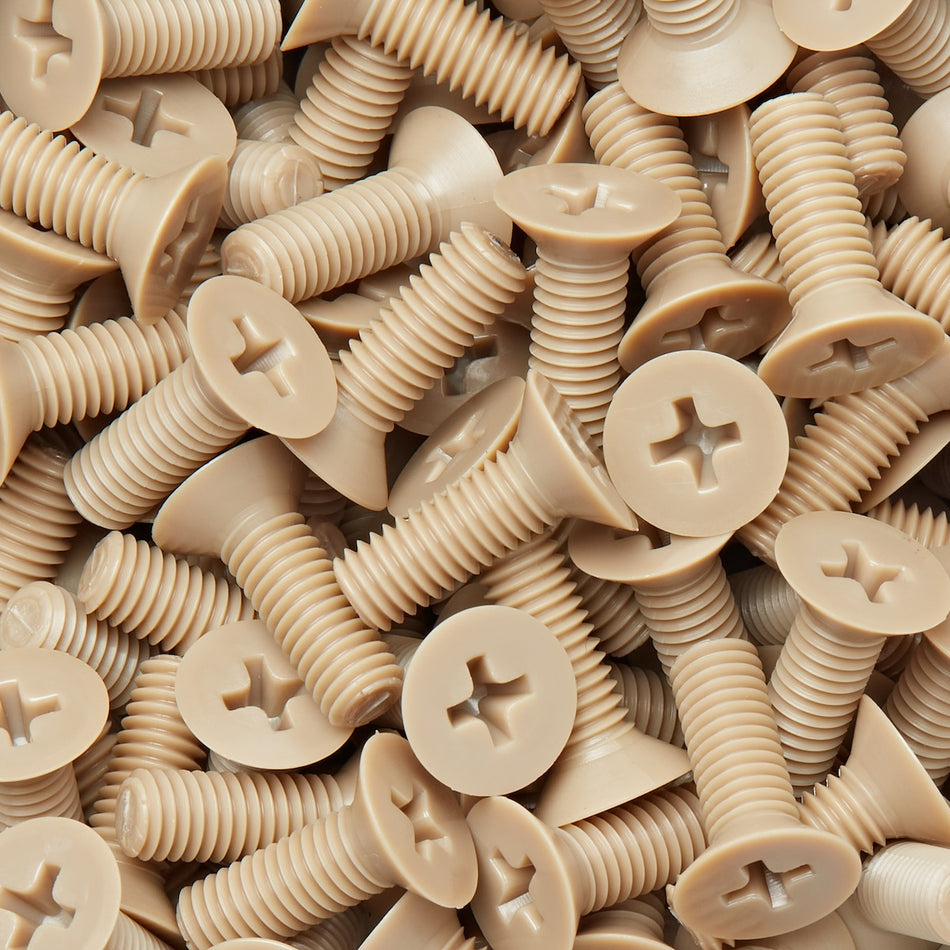
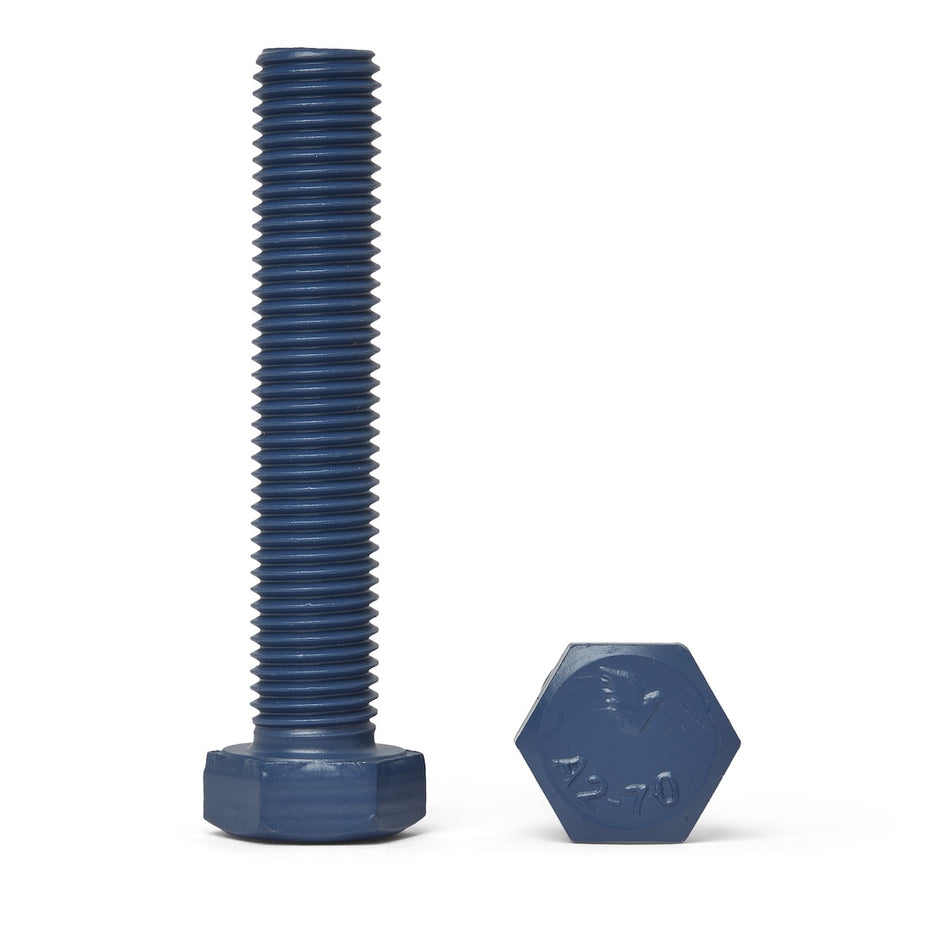
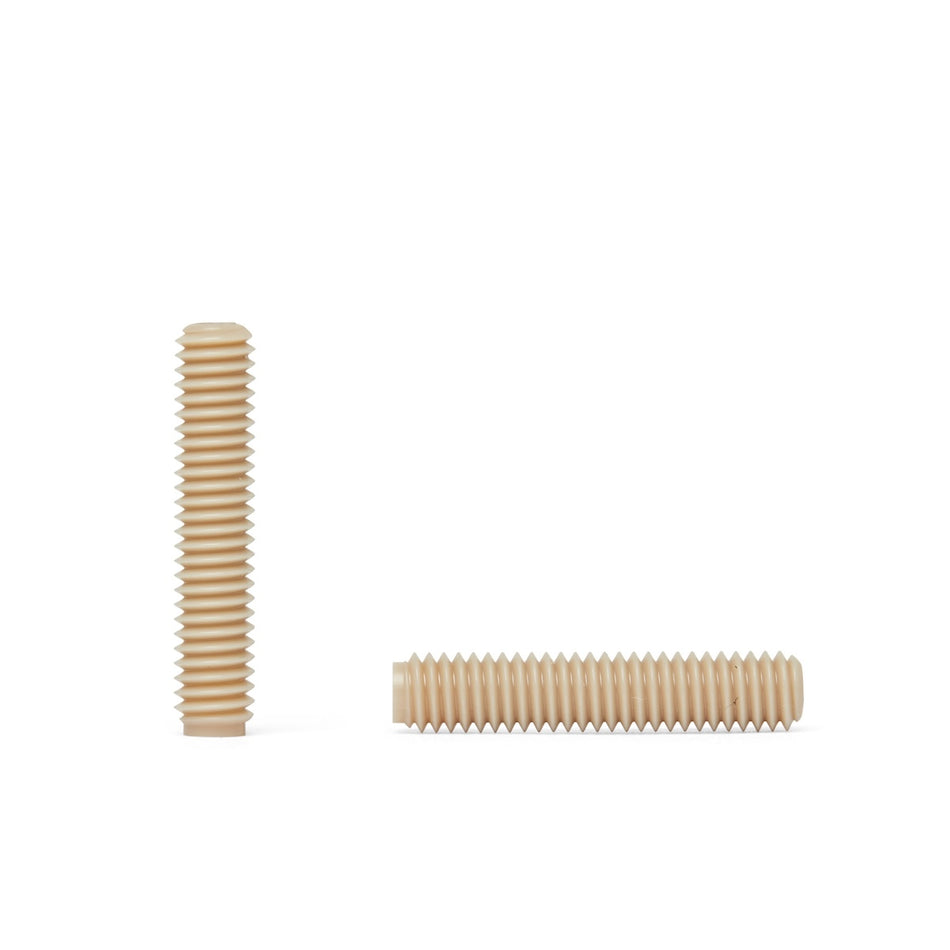
Les vis, écrous, boulons, rondelles et fixations en polymère non magnétique sont des fixations fabriquées à partir de polymères à faible susceptibilité magnétique. Ils sont utilisés dans une variété d'applications où les champs magnétiques sont un problème, comme dans les industries médicales, militaires et aérospatiales, ou dans des environnements où les matériaux magnétiques ne sont pas souhaités.
Il existe une variété de polymères non magnétiques qui peuvent être utilisés pour fabriquer des vis, des écrous, des boulons, des rondelles et des fixations, notamment le polyéthylène, le polypropylène et le polytétrafluoroéthylène (PTFE). Ces polymères sont connus pour leur faible susceptibilité magnétique, ce qui les rend adaptés à une utilisation dans des applications où les champs magnétiques sont un problème.
Les vis, écrous, boulons, rondelles et fixations en polymère non magnétique peuvent être utilisés dans une variété d'applications où les champs magnétiques sont un problème, comme dans la construction d'équipements médicaux ou dans l'assemblage de composants électroniques. Ils peuvent également être utilisés dans la fabrication de matériaux non magnétiques ou dans l'installation de systèmes électriques.
Les fixations en polymère non magnétique sont souvent choisies pour leur faible susceptibilité magnétique, ainsi que pour leurs autres propriétés bénéfiques, telles que la résistance à la corrosion et de bonnes propriétés mécaniques. Ils peuvent aider à améliorer la sécurité et la fiabilité des systèmes médicaux et électroniques, et ils peuvent aider à prévenir les interférences des champs magnétiques.
En plus de leur utilisation dans les industries médicales, militaires et aérospatiales, les attaches en polymère non magnétique peuvent également être utilisées dans d'autres applications où les champs magnétiques sont un problème, comme dans la construction d'appareils d'imagerie par résonance magnétique (IRM) ou dans le fonctionnement des équipements militaires. Ils peuvent également être utilisés dans des environnements où les matériaux magnétiques ne sont pas souhaités, comme dans l'assemblage d'instruments scientifiques ou dans le transport de matériaux sensibles.
































