72 Products
How Polymer Screws, Nuts, Bolts, and Fasteners are used in Scientific instruments
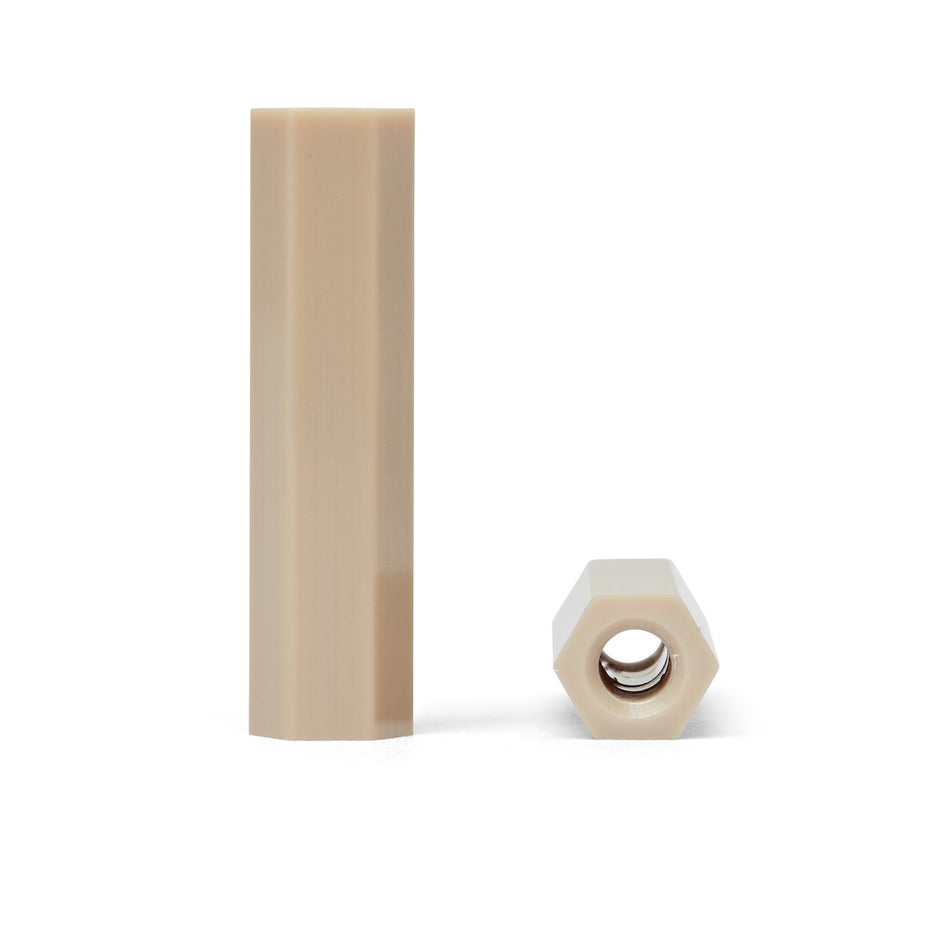
Polymer screws, nuts, bolts, and fasteners may be used in a variety of applications related to the design, construction, and operation of scientific instruments. These types of fasteners are made from a variety of polymers, such as plastic, rubber, or composite materials, and are designed to be strong, durable, and resistant to corrosion.
One potential use of polymer fasteners in scientific instruments is in the construction of the instruments themselves. Polymer fasteners may be used to secure and fasten together the various components and subsystems of a scientific instrument, such as the sensing element, the amplifier, the control electronics, and the housing. Polymer fasteners may be preferred over metal fasteners in certain situations due to their lighter weight and resistance to corrosion.
Polymer fasteners may also be used in the maintenance and repair of scientific instruments. For example, polymer fasteners may be used to secure and fasten together the various parts and components of a scientific instrument housing, such as the top and bottom covers, the sides, and the feet. Polymer fasteners may also be used to secure and fasten together the various parts and components of the control electronics, such as the printed circuit board, the connectors, and the switches.
Overall, the use of polymer screws, nuts, bolts, and fasteners can help to improve the performance, reliability, and durability of scientific instruments, and may play an important role in the design, construction, and operation of these devices.
Scientific instruments are tools that are used to measure, detect, analyze, or control various physical, chemical, or biological phenomena. Scientific instruments are used in a wide range of applications, including scientific research, industrial process control, environmental monitoring, and quality control.
There are many different types of scientific instruments, including:
-
Spectroscopic instruments: These instruments are used to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, such as light or X-rays, and may be based on principles such as absorption, emission, or scattering. Examples include spectrophotometers, spectrometers, and X-ray diffractometers.
-
Analytical instruments: These instruments are used to analyze the composition of samples, and may be based on principles such as chromatography, electrophoresis, or mass spectrometry. Examples include chromatographs, electrophoresis systems, and mass spectrometers.
-
Metrological instruments: These instruments are used to measure various physical quantities, such as length, mass, temperature, or pressure, and may be based on principles such as mechanical, electrical, or optical. Examples include calipers, balances, thermometers, and pressure gauges.
-
Imaging instruments: These instruments are used to generate images of objects or phenomena, and may be based on principles such as optical, magnetic, or radiographic. Examples include microscopes, telescopes, and X-ray machines.
Overall, scientific instruments are an important tool for measuring, detecting, analyzing, or controlling various physical, chemical, or biological phenomena, and are used in a wide range of applications.
































